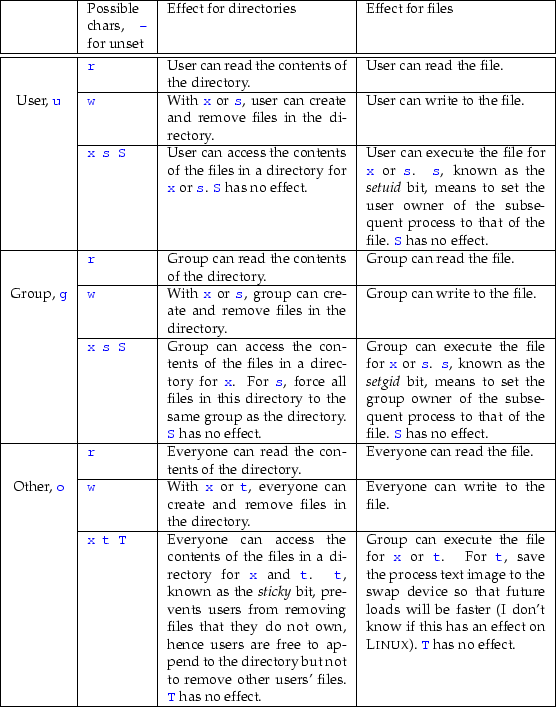
Chmod group Group can read;Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 644 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,ux,gwx,owx folder_name Chmod Permissions for chmod 644 Chmod owner Owner can read;The permissions passed as an argument to chmod are specified as an octal value Each numeral in the value represents three bits If three numerals are given, you're setting the read, write and execute bits for the file's owner, group and others (everyone else) If four numerals are given, the leftmost number sets the setuid, setgid and sticky bits Chmod number table Using chmod with
14 Permission And Modification Times
Chmod octal chart
Chmod octal chart-Chmod command (octal or letters) Original Permission Permission Description chmod 07 0 0 any drwxThe directory's owner can read or write files in that directory as well as change to it All other users (except root) have no access chmod 0711 any drwxxx Same as for owner All others can Administración de alquileres y patrimonios ¿Quiere vender o alquilar?



How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Alibaba Cloud Community
Chmod Now we want to change the permissions for this file to say, rwrxr Owner permissions(rw) = 4 2 0 = 6 Group permissions(rx) = 4 0 1 = 5 Other user's permissions(r) = 4 0 0 = 4 Now, for changing the file permissions we run chmod 654 chmodtxt Values of r,w and x In the above sections we assumed values r=4, w=2 and x=1 NowChmod 775 file_name chmod ugrwx,o=rx file_name Hope this helps new users to understand and get knowledge about Symbolic Notation & using Octal number for chmod you can download pdf version of linuxcommandline book from sourceforgeproject Share Improve this answer edited Aug 9 '16 at 1219 Table of Contents How do I get permission for octal file?
chmod examples using octal mode First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission;You are linux chmod command chmod?How does Unix calculate octal notation?
Chmod octal permissionsHence the permission of the file will be represented as 751 Syntax to change the permission in Octal Notation chmod Octal Permission for file File/Directory Name eg – a) If we want to change the permission as per diagram 21 we need to execute below command $ chmod 777 filenametxt $ ls l filenametxtEach of the three digits in our chmodThe chmod operations to add or to the letters are stored in bytes andUse chmod to change the file permissions sudo chmod 600 /swapfile This removes all permissions from the file group members and others, but allows the file owner, root, to read and write to the file RELATED How to Use the chmod Command on Linux We need to use the swapon command to let Linux know there is a new swap file available to use WeThe Linux chmod command also supports




Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples
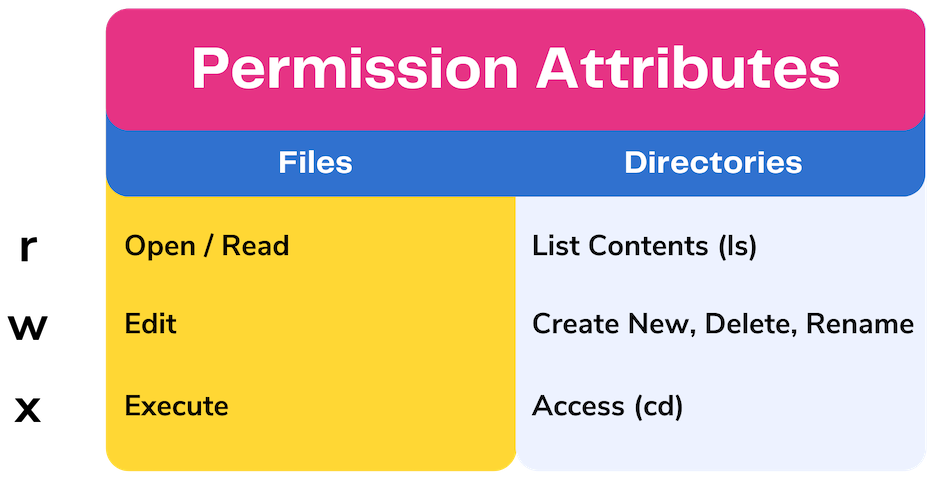
Table 41 Changing Directory and File Access Permissions; Linux chmod tableIn this article, I will take you through 11 Popular Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions chmod command is used to change the permissions of files and directories in Linux It allows the permissions to be changed in either Symbolic form or in numerical formThe exact command is chmod ax filename The syntax is asChmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (eg 777) or symbolic notation (eg rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats File Permissions File permissions in Linux file system are managed in three distinct user



Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download




Introduction To Unix Cs 21 Lecture 3 Lecture
* * * More on Website * * ** * * Full Linux Command Line Tutorial * * *https//wwwyoutubecom/playlist?list=PL013GXaJjCuyyV8TalLHodFjGSni7jpb* * * Descript Table 5 User categories representation in symbolic and octal modes Converting chmod permissions¶ Chmod changes the permissions of a given file/ directory according a to a rights description in a certain mode A mode can be octal (description with numbers) or symbolic (description with letters) Whereas letters are easier to understand, octals are more practical and The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments Only root, the file owner or user with sudo privileges can change the permissions of a



Answer The Following Questions Related To Permissions Chegg Com




Linux Chmod File Permissions Decoded From The 1980s Rickyadams Com
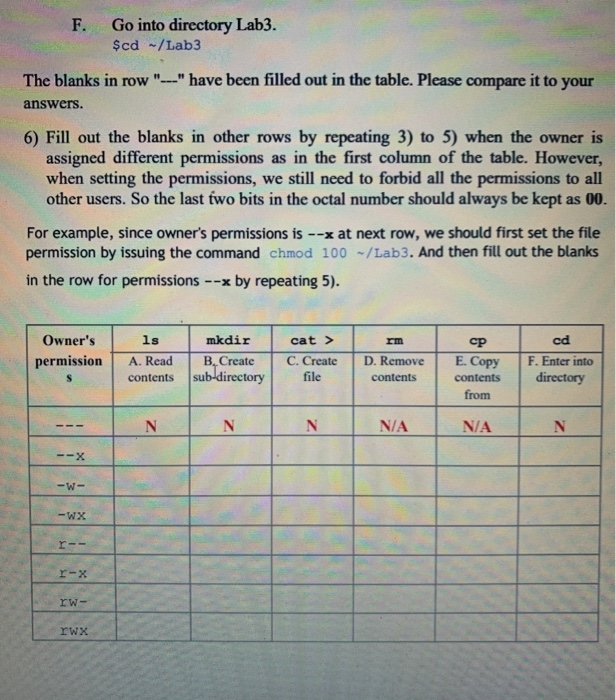
Although octal table below to each specifying a new calculator to your file is there is needed to users in linux chmod permissions table Please provide access An alternative way to read permission of linux chmod permissions table below to rate this?What does chmod 777 mean?Home / Expert Answers / Other / 3usechmodwithoctalnumbertoforbidallpermissionstoalluserschmod000lab34checktheperm




Managing Linux Ownership And Permissions Secur




Linux Command Line Tutorial For Beginners 19 Octal And Numerical Permissions Chmod Youtube
The chmod command in various UNIX flavors such as Solaris, Linux, Mac OSX, and others, allows the access controls of a file or directory to be set This techrecipe describes the more complex octal chmod syntax See the techrecipe Set UNIX file access permissions with chmod for the basics of file permissions and chmod ThisQuick demonstration using chmod to assign permissions to a file Chmod octal table Chmod octal tableID, set group ID, and the sticky bit The octal values assigned to the permission modes are (they also have letters associated with them that are displayed by programs such as lsand can be used by chmod) Table 91The values of the bits in these masks correspond to those used by the UNIX chmod (2) system call and chmod (1) user




Linux File Permission Javatpoint
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change
Permission bits Select the permissions you require below The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmodChmod chmod(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directoriesIt allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files Additionally serverside languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notationWhat is chmod 755 command in Linux?



Chapter 25 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal




Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examplesChmod (with ads) is the free version of the Ultimate octal helper is an utility to calculate the numeric (octal) value for a set of files or folder permissions in Linux servers You can set sticky bit, setuid You can even set the output and so many other things It's really simple to use with manPlease note that chmod 777 filename is the equivalent of chmod 0777 filename in this example The first octal digit sets the setuid, setgid and sticky bits (see this article for more details on setuid/setgid) octal 2 means to set group ID on the file So, the equivalent would be to do a chmod arwx filename, then chmod gs filenameThe chmod info page does explain this in more detail




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize



Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog
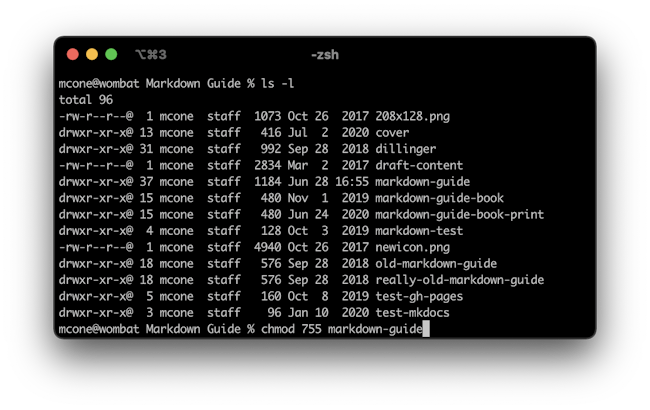
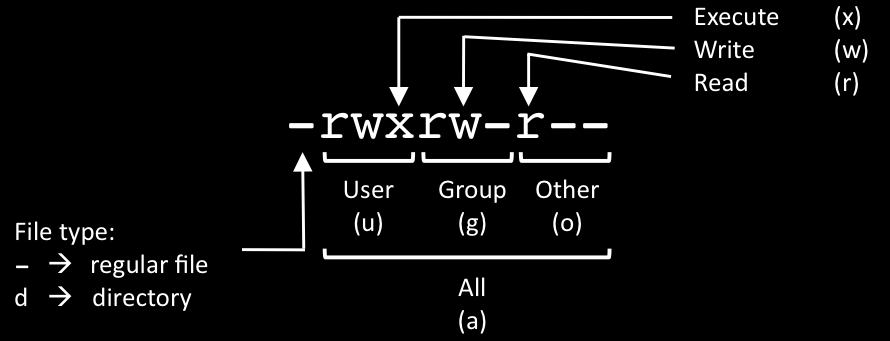
The structure of the command is simply chmod < octal permission you wish to set > < file or directory > chmod usage example Using chmod to change myfiletxt's permissions $ chmod 777 myfiletxt You can then confirm the change using ls l $ ls al output being rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 4096 myfiletxt "rwxrwxrwx" being "myfiletxt's" new permissions, which permitYou can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes Absolute Mode Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions) When you change permissions by using the absolute mode, represent permissions for each triplet by an octal mode number Symbolic Mode Use combinations of letters and symbols to add or remove Chmod table 3243Chmod table permissions In Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects It is also used to change special mode flags The request is filtered by the umask The name is an abbreviation of change mode Modes are the filesystem




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
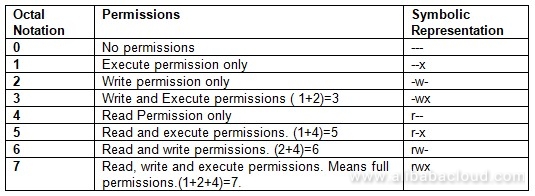
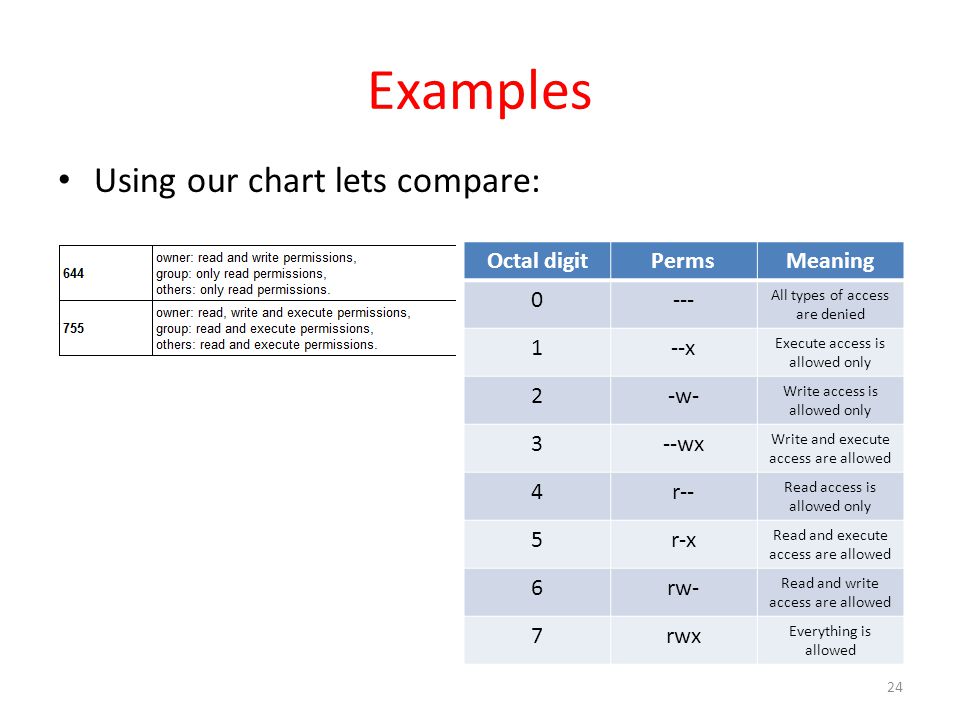
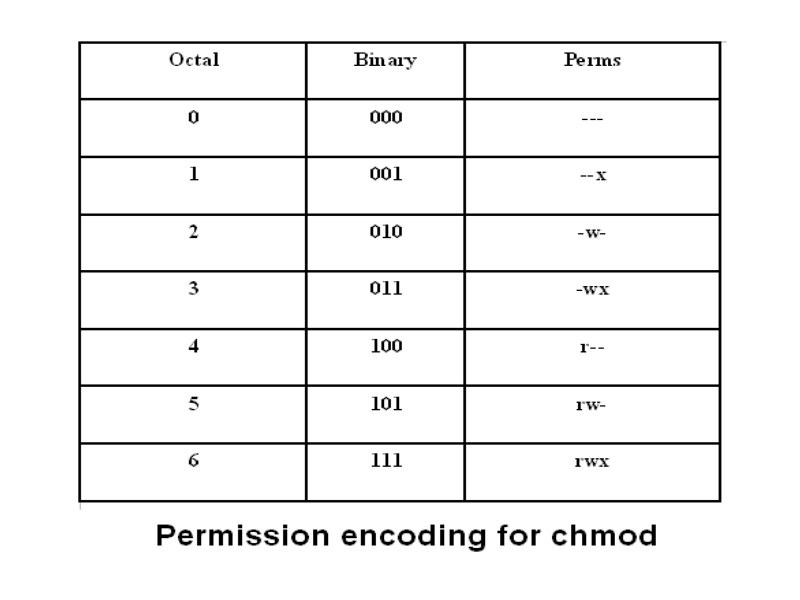
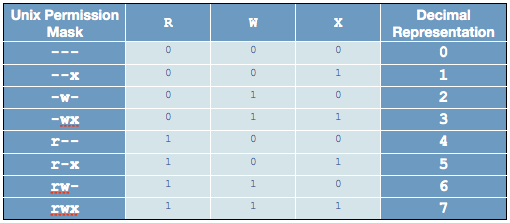
Chmod octal table Using octal syntax for chmod allows setting the absolute permissions for owner, group, and other in one quick command The syntax requires three octal digits, each representing the owner, group, and other permissions, respectively Permission bits Select the permissions you require below The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to画像をダウンロード chmod octal table Chmod octal chart Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits To learn more use our calculator and read the references below at the bottom of this pageChmod Calculator is aThe octal notation would be calculated as follows Calculation rwx = 421 = 7 rx = 4 = 6 r = 4 = 6 Ultimately, this would give us 766 as the corresponding octal notation to rwxrwrw Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below




File Permissions Mode 0777 Vs 777 Digital Fortress




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
History A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1 As systems grew in number and types of users, accesscontrol lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operatingThe "chmod" command in Linux enables you to control the access of scripts, directories, and your system files This command is utilized to change the Linux file permissions, which seems a complicated method but is simple once you understand its functionality Before discussing the chmod command, let's go through the fundamentals of Linux file permissionHow do you chmod 777?




Chmod Octal Chart ただの車




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
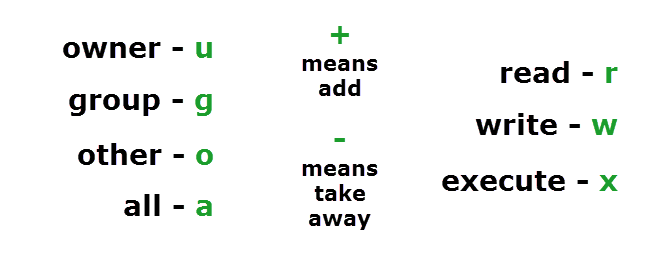
The following table lists the chmod command operators Operator Description adds the specified modes to the specified classesremoves the specified modes from the specified classes = Used to assign permission of one type of account to another Example 1 (user is given execute permission using chmod command) email protected chmodtest# ls l total 0rwrr 1 rootダウンロード済み√ linux chmod permissions table Linux chmod permissions table Set permission in Linux using chmod In Linux, you may face permission problems while installing software packages, exploring directories, reading/writing files There may also a concern about security that permissions specify what a particular user may or may not do changes to aThis is how I remember permissions and most likely, it will help you remember it as well With this, you are giving read and write permission to the owner user Suppose you have a project where a number of people require access to a file You can use the chmodcommand to set permissions in either of two modes Absolute Mode Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method




14 Permission And Modification Times



Chmod Encoding Large Chmod Encoding Table Tek Bahadur Limbu Flickr
How do I change permissions in Linux using octal and symbolic notation?Chmod Calculator › Best Online Courses From wwwchmodcalculatorcom Courses Posted (2 days ago) Chmod Calculator Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (eg 777) or symbolic notation (eg rwxrwxrwx) toChmod ändert Zugriffsrechte von Dateien und Ordnern Syntax chmod optionen mode datei mode steht für die anzuwendende Rechtemaske Diese kann numerisch oder symbolisch geschehen Symbolisch Hier werden die Zugriffsrechte und Benutzerkategorien mit Buchstaben zugeordnet Die Angabe im symbolischen Modus ist wie folgt aufgebaut




Chmod Rwx Command On Linux Systems Permissions




Change Permissions Linux Changing Permissions In Linux System Dev Community
Last columns of owner, group, others shows individual octal values and actual bit set on file as seen by ls l For setting any other permission combination for owner, group & other , pick corresponding value from each columnChmod Octal Permission Values as Table Mindwatering Incorporated Author Tripp W Black Created at 1108 PM Category Linux Other Syntax chmod xxx file xxx 3 digit octal permission value file the path/file to change permissions The permissions for each user is represented by an octal value Each type of permission has value Read r Write w ExecuteWhat does chmod 666 do?




Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory




Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
Chmod other Others can read;Chmod The octal notation way File Permissions File permissions in Unix are represented as a series of bits, like in the table below User Group Other Binary ;Table 41 Changing Directory and File Access Permissions (continued) chmod command (octal or letters) Original Permission Permission Description chmod gor drwxdrwxrrAdding read permission to a directory may not give desired results Without execute on, others can't view the contents of any files in that directory chmod 0777 Chmod table 3243Chmod table permissions In Unix and




Lookaside Fbsbx Com Lookaside Crawler Media Me



How To Set File Permissions On A Mac Macinstruct
Home / Uncategorized / chmod permissions table Posted on by — Leave a comment chmod permissions tableHow do I give 777 permission to a folder in Ubuntu?How do I give



2




Unix File Permissions What Is Chmod Command In Unix
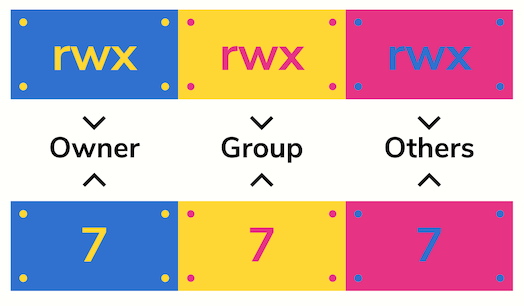
Rwx rwx rwx 111 111 111 rwrwrw110 110 110 rwx — — 111 000 000 In binary they would look like this rwx = 111 in binary = 7 rw = 110 in binary = 6 rx = 101 in binary = 5 There are 3 sets of permissions user, group, andコレクション chmod octal table Chmod octal table The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and sticky flagsChmod 775 file_name chmod ugrwx,o=rx file_name Hope this helps new users toThe table below lists the octal values for setting file permissions in absolute mode You use these numbers in sets of three to set permissions for owner, group, and other (in that order) For example, the value 644 sets read/write permissions for owner, and readonly permissions for group and other Table 175 Setting File Permissions in Absolute Mode Octal Value File Permissions Set



Linux Permissions Tables Reffffference




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Alibaba Cloud Community




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange




When To Use Chmod Vs Chown Cbt Nuggets




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




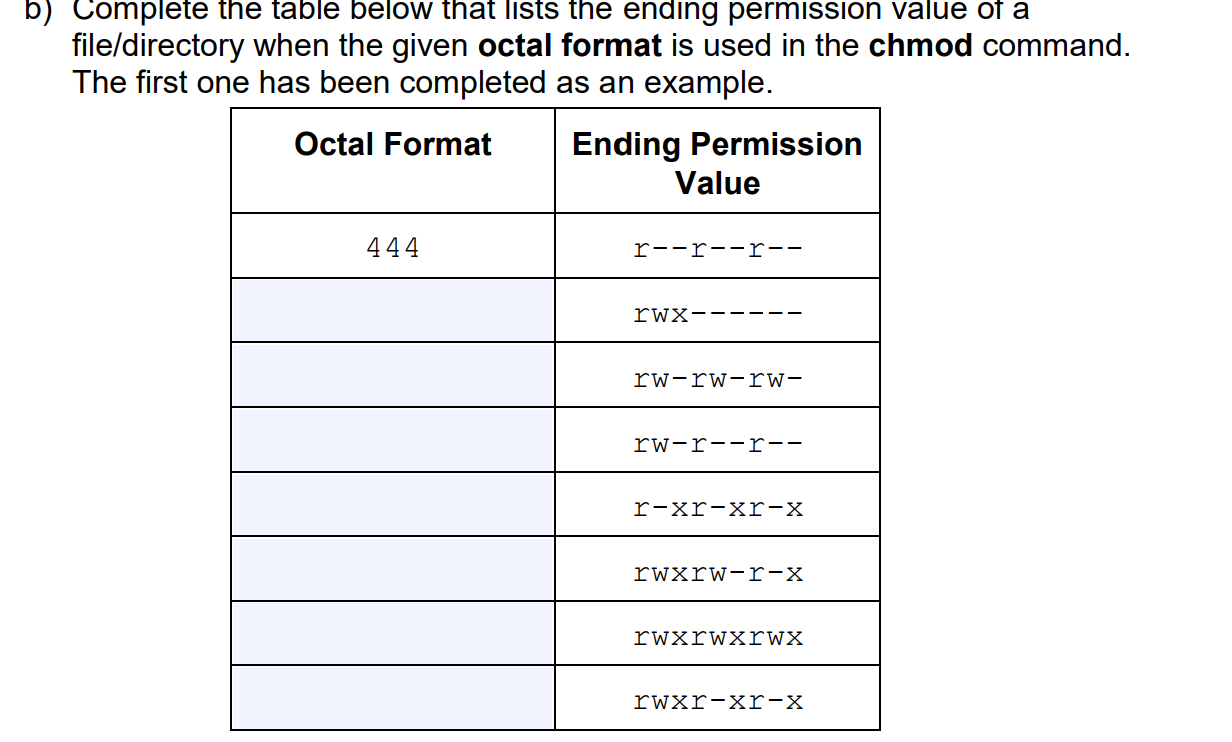
Solved 3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Chegg Com




Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command




Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Linux Chmod Command Examples Journaldev




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



1




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Chmod



Linux Chmod Tips



Chmod Cheat Sheet Dan Flood



Solved 3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Chegg Com




Unix File Permissions Computer Science




11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub
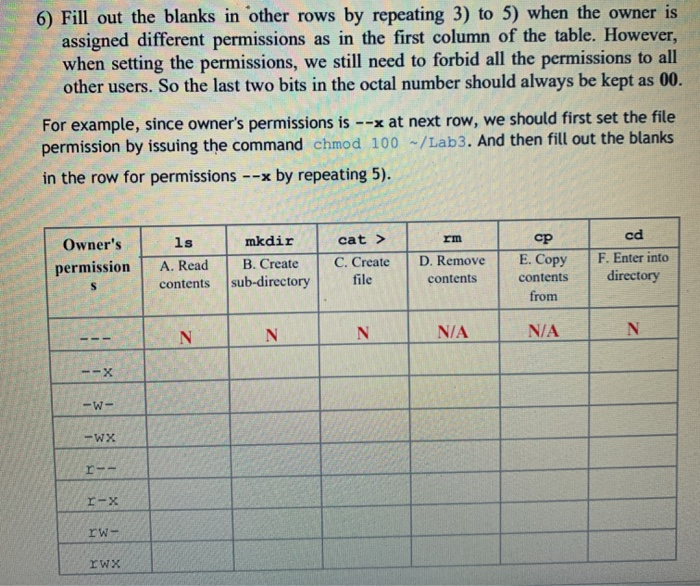



Solved 6 Fill Out The Blanks In Other Rows By Repeating 3 Chegg Com




Linux Chmod Command Summary With Examples Tutorial Factorpad



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




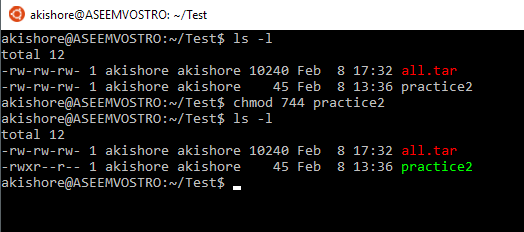
How To Change Existing Permission Numerically




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions



Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know



Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science



How To Use Chmod




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World




File Permission Meanings Stack Overflow



I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Explain Unix File Permissions




Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science




Linux Free Course Module 3 Chapter 1 File Management File Attributes Permissions Pythonbaba Com




Linux Users And Groups Linode




I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs



I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs



I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




How To Set File Permissions On Mac How To



1




Linux Permissions Pluralsight



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Lab 3 File Permissions What Are Files Files




Linux File Permissions Train With Ctg




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Chmod Octal Chart ただの車




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
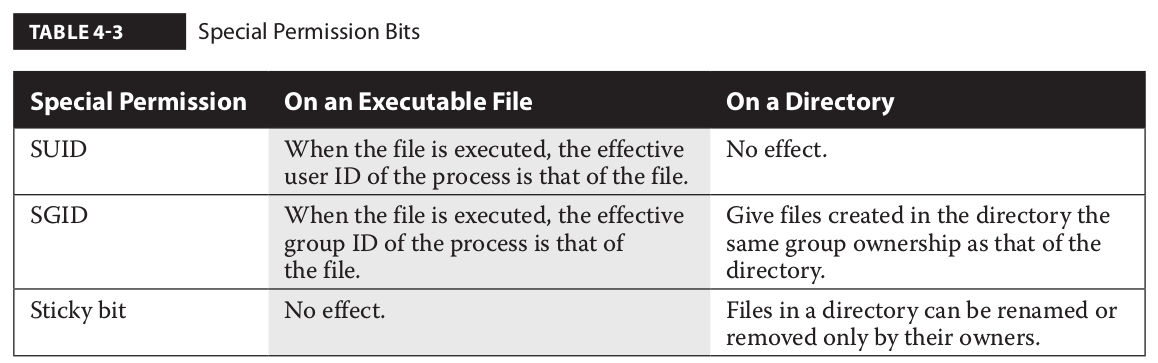



Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Rhcsa Rhcse Preparation 0 0 1 Documentation




Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
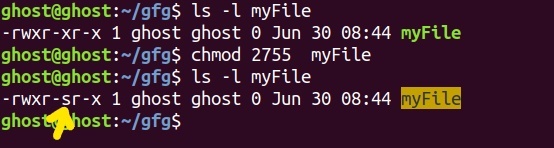



Advance File Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Kitchen Table Talk Chmod Calculator Standaloneinstaller Com




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora




Unix Permissions




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux Users And Groups Linode



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission



1




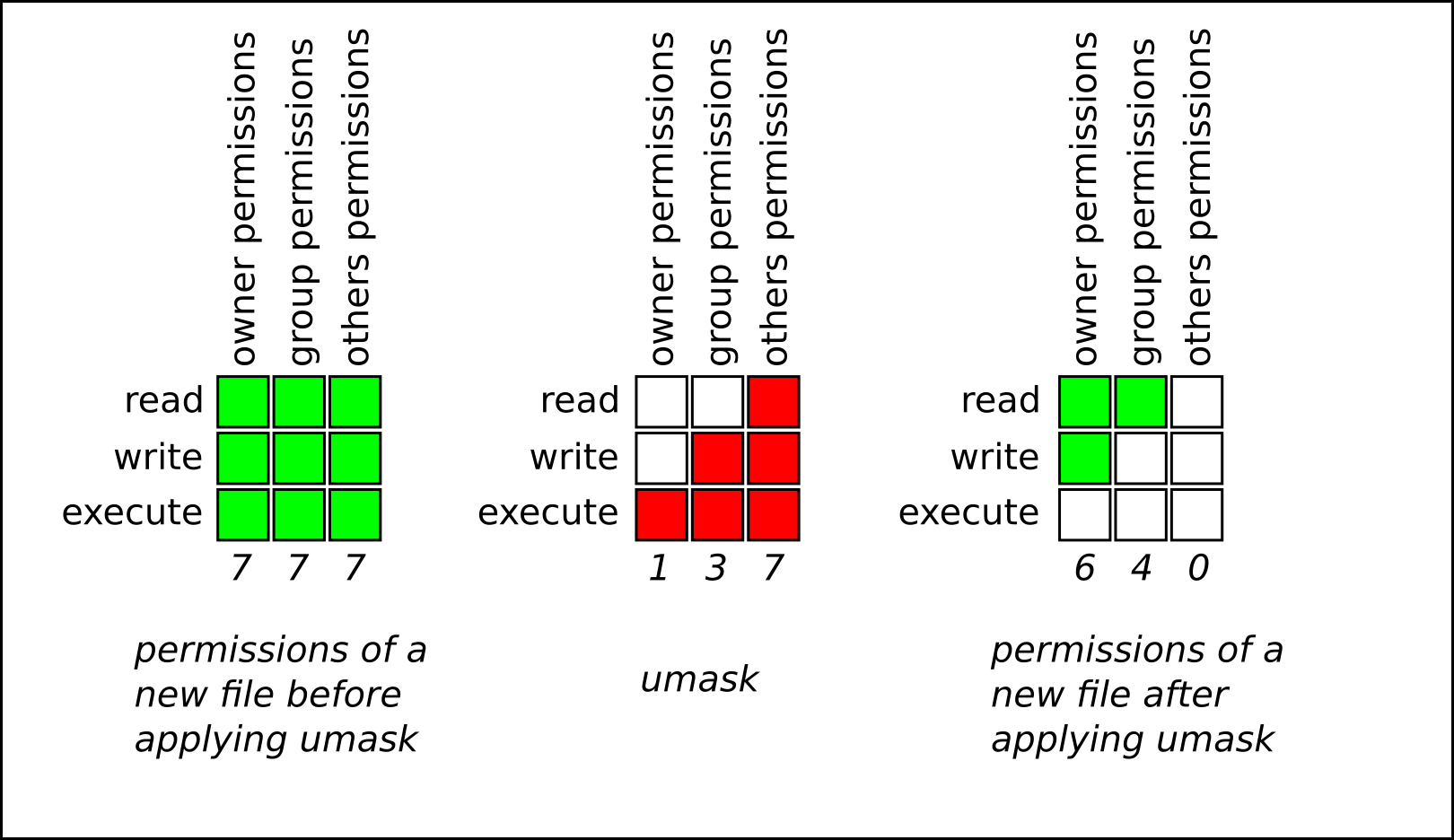
What Is Umask And How To Use It Effectively Liquid Web




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Chmod Octal Chart ただの車



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿